Resource Manager¶
Abstract
The Resource manager is a Gateway service that allows a user to manage data inside a distant storage. The user can
upload, download, list, delete, move, copy or register data files using a REST client through the /resources
Gateway's endpoint.
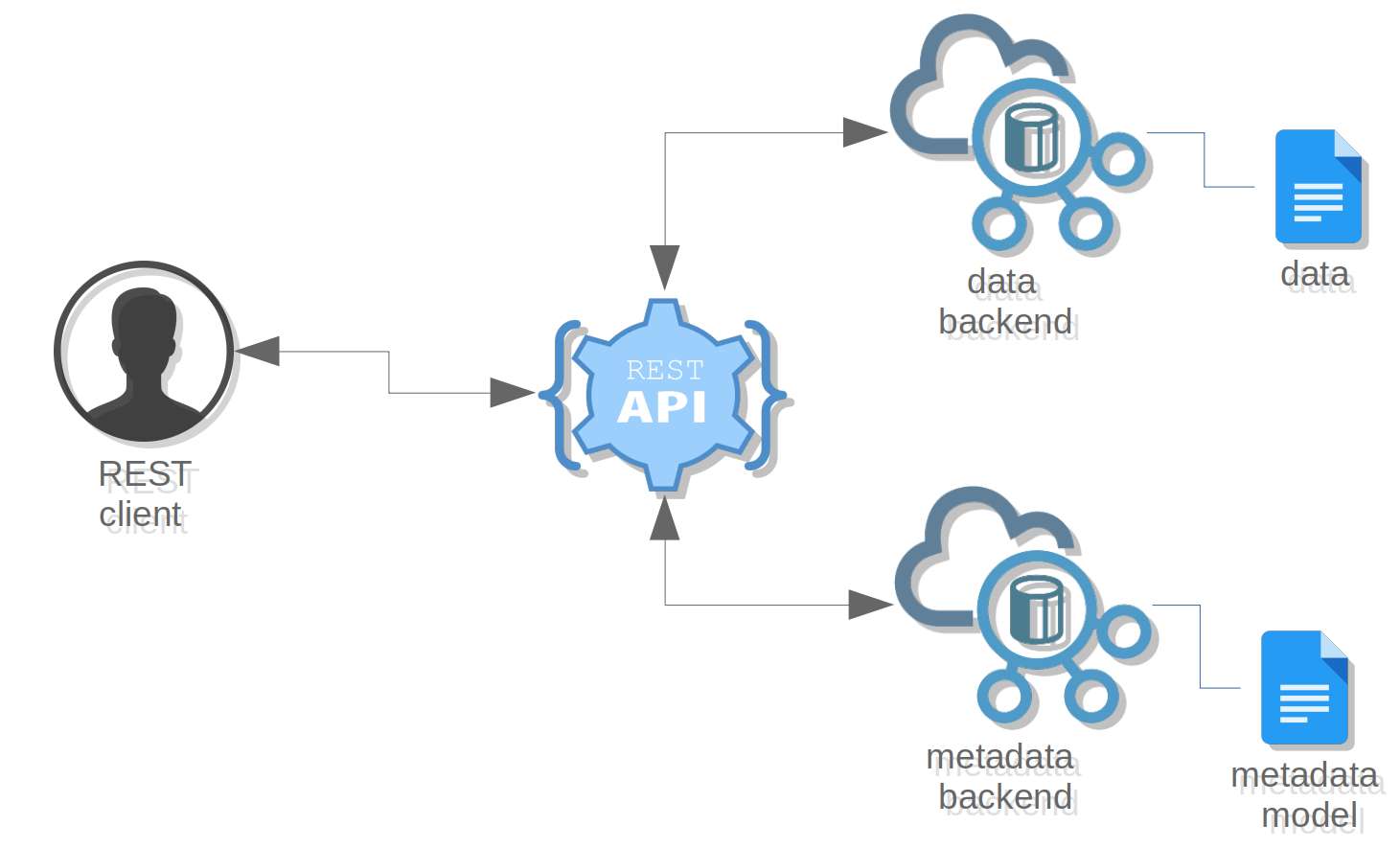
The Resource manager is divided into two types of backends :
- metadata storage backend
- data storage backend
How it works¶
A REST client can perform multiple actions from the Resource Manager :
- Upload a resource
- Download a resource
- Copy a resource
- Move a resource
- Delete a resource
- List resources
- Register an external resource
Every action is performed for a dedicated tenant defined by the gateway.
Example : List all resources of mytenant
curl -L -X GET 'http://localhost:4242/v1/mytenant/resources/list?simplify=true'
{
"metadata": [
{
"@timestamp": "2020-10-09T12:36:39.107Z",
"name": "datasets/dataset_generator",
"version": 2
},
{
"@timestamp": "2020-10-09T12:37:44.785Z",
"name": "datasets/batch_input",
"version": 0
}
],
"name": "*",
"message": "List resources",
"tenant": "mytenant"
}
Metadata Storage¶
The metadata storage is used to store information about the uploaded data.
A metadata is basically a key:value model containing diverse information :
| key | value |
|---|---|
schema |
Version of the current metadata model |
name |
Name of the uploaded data.The name can be a resource path or a simple name. It may contain a file extension but it has no effect on data content. Can be different from the storage.url of the data inside the data storage |
timestamp |
Time of the last data update or creation |
version |
Version of the uploaded data. This number increases when the same data is uploaded multiple times |
tenant |
Tenant of the uploaded data. Each data is possessed by one tenant |
size |
Byte length of the uploaded data |
storage.type |
Type of the data storage of the uploaded data. For example, if file is the storage type, it means the data is contained inside a filesystem |
storage.url |
Real location of the uploaded data inside the data storage |
storage.encoding |
Optional. Data encoding inside the data storage |
storage.compression |
Optional. Version of the uploaded data. This number increases when the same data is uploaded multiple times |
storage.data |
Optional. Version of the uploaded data. This number increases when the same data is uploaded multiple times |
properties |
Optional. Custom Map. The user can put additional key-values in metadata. These properties are useful to filter requested data for research purposes |
Info
Check how to configure metadata storage for deployment: deployment settings documentation
Elasticsearch Metadata Storage¶
The Elasticsearch metadata storage type uses an index to store metadata.
Configuration :
manager:
metadata:
elasticsearch:
- hosts:
- "localhost:9200"
index_name: "resources-metadata"
The metadata index name is prefixed by the Punch Gateway's tenant name to ensure the resource partitioning.
The Elasticsearch metadata is a document where each model key is a field of the document.
Example :
{
"schema": "V1",
"name": "/my/resource",
"timestamp": "1602230389 ",
"version": "2",
"tenant": "mytenant",
"size": "2048",
"storage": {
"type": "file",
"url": "/data/resources/mytenant/my_resource.hjson"
},
"properties": {
"author": "bob",
"editor": "vim"
}
}
Data Storage¶
The data storage is used to store the resource content itself.
Info
Check how to configure data storage for deployment: deployment settings documentation
File Data Storage¶
The file data storage type uses a filesystem to store the resources.
Configuration :
manager:
data:
file:
- root_path: "/tmp/punchplatform/manager/resources"
Every data will be stored inside :
<root_path>/<resource_name>
The url of a resource is then a filesystem path where the resource version is injected. For the first upload of a resource, the url will be :
<root_path>/0/resource
Info
The name of the resource can be a path : my/resource.txt will be store inside <root_path>/my/0/resource.txt
Metadata Transparency¶
Metadata transparency is the key concept of the Resource Manager.
Each client action results in an automatic operation on metadata without any additional action from this client.
Every new uploaded data or new uploaded version of the same data is resulting in a metadata generation. No action is needed from the client : the metadata is automatically generated and pushed inside the metadata backend storage.
In the same way, any request to list, download, delete, copy or move a resource will automatically look for the resource metadata first to obtain the resource information and then proceed to the requested action from the client.
| Client action | Data |
|---|---|
| Upload | The data is uploaded then a resource metadata is automatically created |
| Download | The resource metadata are automatically requested then the data is returned using the resource url inside the metadata |
| Delete | The resource metadata are automatically requested then the data is removed using the resource url inside the metadata. The resource metadata is finally removed too |
| List | The resource metadata are returned |
| Copy | The resource metadata are automatically requested then the data is uploaded to the new location |
| Move | The resource metadata are automatically requested then the data is copied to the new location. Finally, the original data is removed and the resource metadata is deleted |
| Register | The resource metadata is pushed inside the metadata storage |